How Heat Affects Protein Ingredients
Heat is used at various stages of protein ingredient production. Its role is primarily functional, supporting separation, drying, and stabilization rather than changing what protein is at a biological level.
This article explains how heat affects protein ingredients using clear, foundational language. The focus is on physical and structural effects rather than outcomes, performance, or recommendations.
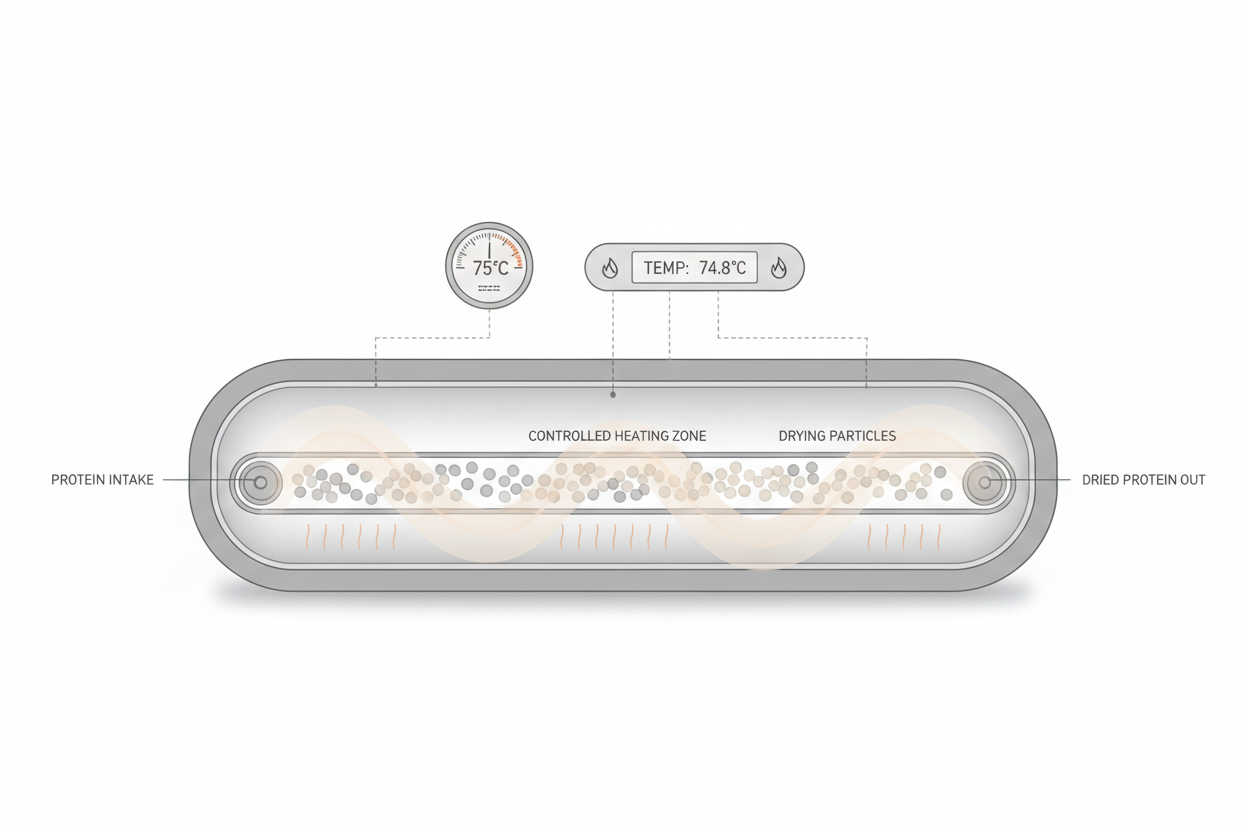
Heat Is Used During Processing Steps
Heat is applied during specific processing stages.
Common uses include aiding separation, supporting drying, and helping convert liquid protein solutions into stable powder form. Heat is applied in controlled ways designed to support manufacturing needs.
These steps occur before protein reaches the consumer and are part of standard ingredient production.
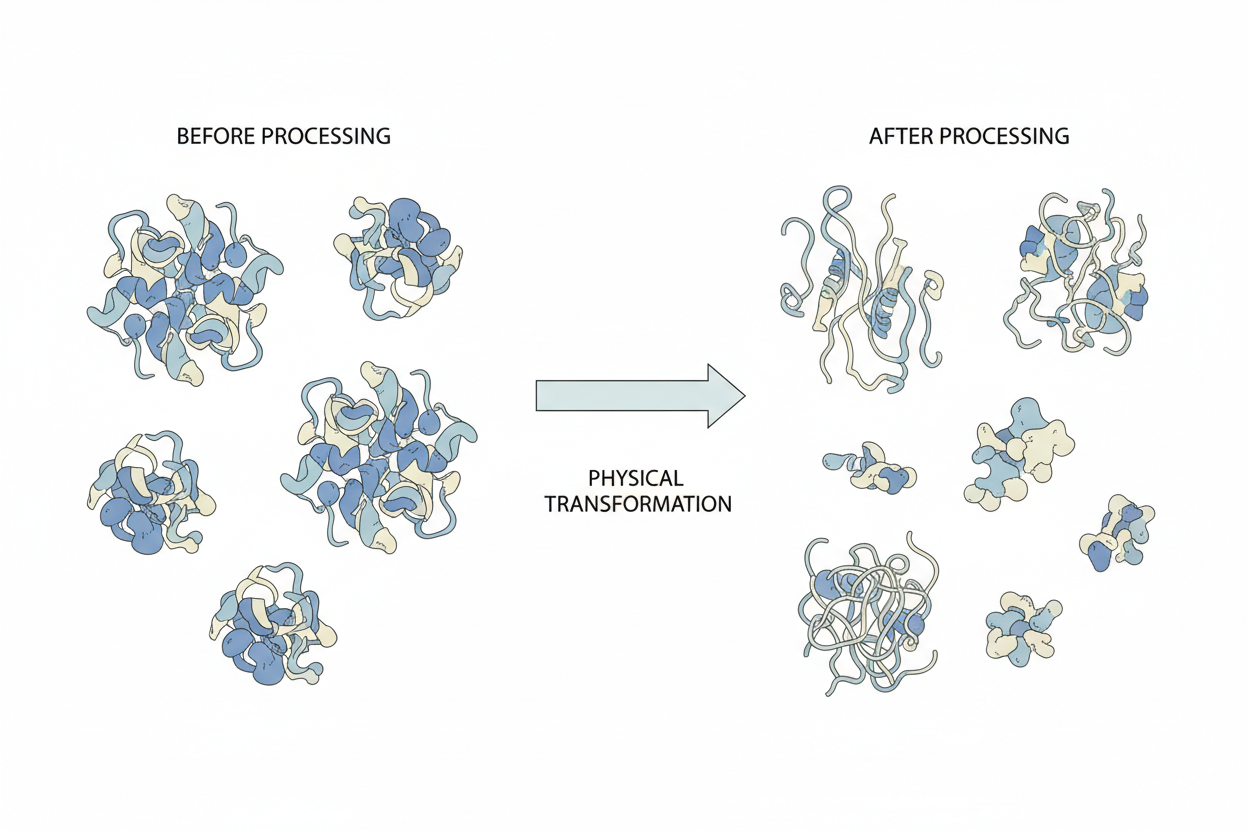
Heat Can Influence Protein Structure
Protein molecules have physical structure that can respond to heat.
When heat is applied, protein molecules may change how they fold or interact with one another. These changes affect physical arrangement rather than amino acid composition.
The protein remains protein. The amino acids that make it up do not change.
Heat and Protein Solubility
Heat can influence how protein behaves in water.
Depending on processing conditions, heat exposure may affect how protein particles interact with liquid during mixing. This can influence characteristics such as dispersion or consistency in powdered form.
These effects matter for formulation and handling rather than digestion or biological use.
Controlled Heat Versus Excess Heat
Protein processing uses controlled heat.
Temperatures and exposure times are selected to support processing goals while maintaining ingredient stability. Excess or uncontrolled heat is avoided because it can interfere with manufacturing consistency.
This balance helps ensure protein ingredients remain predictable and usable.
Heat Effects Occur Before Digestion
Heat affects protein ingredients before they are consumed.
Once eaten, protein is broken down into amino acids during digestion regardless of prior heat exposure. Heat related structural changes do not alter how amino acids are ultimately used by the body.
This distinction helps separate processing effects from biological function.
Heat and Ingredient Stability
Heat can contribute to ingredient stability.
Drying steps that involve heat remove moisture, which helps extend shelf life and reduce variability. Stability refers to physical consistency over time rather than biological activity.
Heat plays a role in achieving that stability during production.
How This Fits Into Protein Fundamentals
Protein Fundamentals explains how protein moves from source to use.
Understanding how heat affects protein ingredients adds context to processing and structure topics without shifting into evaluation or claims. It explains physical changes that occur before digestion as part of the ingredient lifecycle.
The explanation remains grounded in structure and process.
Part of the Nutrition Foundations Series
This article is part of our Nutrition Foundations series, where we explain how different macronutrients are digested and used by the body.
👉 Visit the Nutrition Foundations hub to explore more articles in this series.
Related Articles in This Series
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Does heat change amino acids
A: No. Heat affects physical structure, not amino acid composition.
Q: Is heat always used in protein processing
A: Many processing steps involve heat, but methods vary by ingredient and goal.
Q: Does heat affect digestion
A: Digestion breaks protein into amino acids regardless of prior heat exposure.
Q: Is heat used to sterilize protein ingredients
A: Heat may support processing and drying, but this article focuses on structural effects.
Q: Can heat affect protein texture
A: Yes. Heat can influence physical characteristics such as consistency and solubility.
Q: Does this article evaluate heat processing
A: No. It explains how heat interacts with protein ingredients.